
04 Jan GEOMETRY TUTORING
NYC GEOMETRY TUTORING

Our GEOMETRY tutors travel to YOUR home:
We also travel to:
Module 1: Plane Geometry
Topic A: Introduction to Geometry
Plane Geometry is about flat shapes like lines, circles, and triangles … shapes that can be drawn on a piece of paper.
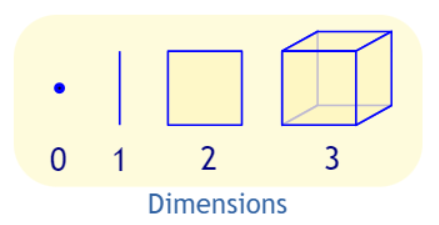
Point, Line, Plane and Solid
A Point has no dimensions, only position
A Line is one-dimensional
A Plane is two dimensional (2D)
A Solid is three-dimensional (3D)
Plane Geometry is all about shapes on a flat surface (like on an endless piece of paper).
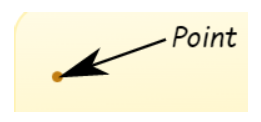
Let us start with a point. A point has no dimensions.
A point really has no size at all! But we show them as dots so we can see where they are.
Now let’s allow the point to move in one direction. We get a line.
We need just one value to find a point on that line. So we have one dimension. A line is one-dimensional.
Now let’s allow the point to move in a different direction. 
Circles, triangles, squares, and more are plane shapes.
We let that point move in another completely different direction, and we have three dimensions.
Spheres, cubes, cylinders, and more are 3-dimensional or “3D”. We also call them solid shapes.

We can have more dimensions (such as this 4D Tessaract) in mathematics, but they are hard to draw!
2D Shapes
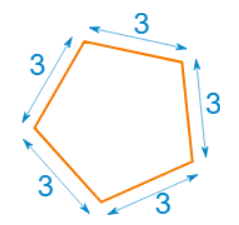
A polygon is a plane (2D) shape with straight sides. To be a regular polygon, all the sides and angles must be the same:
Other Common Polygons
These are 2D shapes, and they are polygons, but not regular polygons:
Quadrilateral
Any 4-sided 2D shape
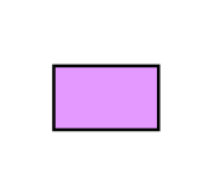
Rectangle – 4 Sides
All right angles
Triangles
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted \triangle ABC. In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non-collinear, determine a unique triangle and simultaneously, a unique plane. It can be classified into three: Equilateral, Isosceles, and Scalene.
There are three special names given to triangles that tell how many sides (or angles) are equal. There can be 3, 2, or no equal sides/angles:
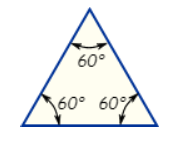
Equilateral Triangle
Three equal sides; Three equal angles, always 60°
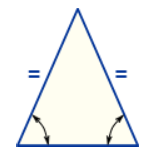
Isosceles Triangle
Two equal sides; Two equal angles
Scalene Triangle
No equal sides; No equal angles
How to remember? Alphabetically they go 3, 2, none:
- Equilateral: “equal”-lateral (lateral means side) so they have all equal sides
- Isosceles: means “equal legs”, and we have two legs, right? Also isosceles has two equal “Sides” joined by an “Odd” side.
- Scalene: means “uneven” or “odd”, so no equal sides.
What Type of Angle?
Triangles can also have names that tell you what type of angle is inside:
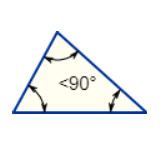
Acute Triangle
All angles are less than 90°
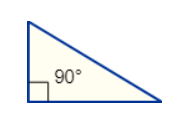
Right Triangle
Has a right angle (90°)
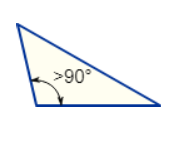
Obtuse Triangle
Has an angle more than 90°
Combining the Names
Sometimes a triangle will have two names, for example,
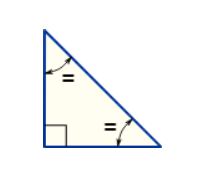
Has a right angle (90°), and also two equal angles
Topic B: Perimeter
Perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape.
Example: the perimeter of this rectangle is 7+3+7+3 = 20
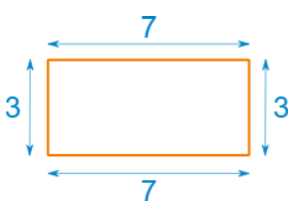
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 5×3 = 15
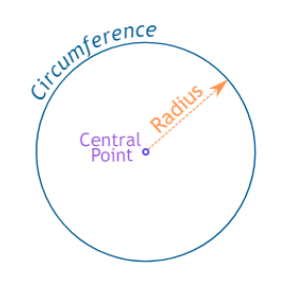
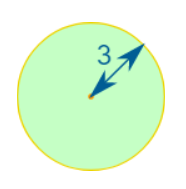
The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference:
Circumference = 2π × radius
Perimeter Formulas
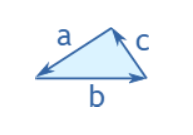
Perimeter = a + b + c
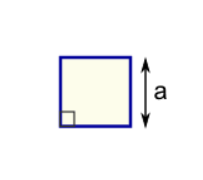
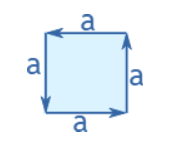
Square
Perimeter = 4 × a
a = length of side
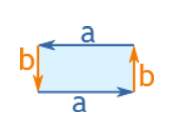
Rectangle
Perimeter = 2 × (a + b)
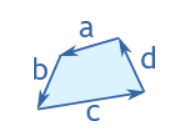
Quadrilateral
Perimeter = a + b + c + d
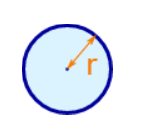
Circle
Circumference = 2πr
r = radius
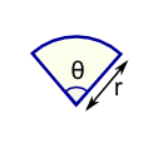
Sector
Perimeter = r(θ+2)
r = radius
θ = angle in radians
Ellipse
Perimeter = very hard!
Topic C: Area
Area
Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or a curved surface. The area of a plane region or plane area refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while surface area refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-dimensional object.
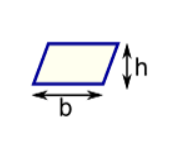
Parallelogram
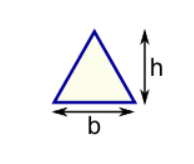
Area = b × h
b = base
h = vertical height
Area = ½(a+b) × h
h = vertical height
Circle
Area = π × r2
r = radius
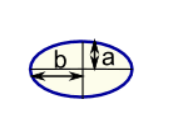
Area = πab
Sector
Area = ½ × r2 × θ
r = radius
θ = angle in radians
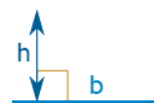
Note: h is at right angles to b
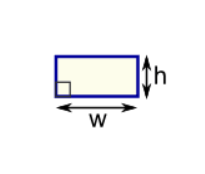
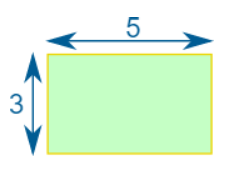
Example: What is the area of this rectangle?
The formula is:
Area = w × h
w = width
h = height
We know w = 5 and h = 3, so:
Area = 5 × 3 = 15
Example: What is the area of this circle?
Radius = r = 3
Area
= π × r2
= π × 32
= π × (3 × 3)
= 3.14159… × 9
= 28.27 (to 2 decimal places)
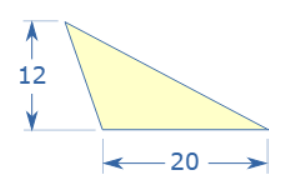
Example: What is the area of this triangle?
Height = h = 12
Base = b = 20
Area = ½ × b × h = ½ × 20 × 12 = 120
Word Problem:
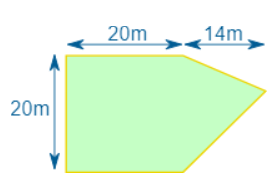
Example: Sam cuts grass at $0.10 per square meter How much does Sam earn cutting this area:
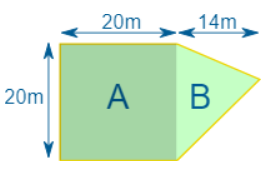
Let’s break the area into two parts:
Part A is a square:
Area of A = a2 = 20m × 20m = 400m2
Part B is a triangle. Viewed sideways, it has a base of 20m and a height of 14m.
Area of B = ½b × h = ½ × 20m × 14m = 140m2
So the total area is:
Area = Area of A + Area of B = 400m2 + 140m2 = 540m2
Sam earns $0.10 per square meter
Sam earns = $0.10 × 540m2 = $54
TESTIMONIALS
We have been with our tutor, Cailin, for two years, from 5th – 7th grade. She started as an executive functioning tutor with my daughter. From the start, she demonstrated a depth of expertise and a selective use of techniques skillfully adapted to my daughter’s ADHD and mth disability. Cailin made math accessible and understandable to her in a way that even her teachers had not been able to do. She differentiated reading, writing and math tasks and assignments to tailor them to my daughter’s unique learning differences. Not only did it have an effect on her grades and her work efficiency, but she finally could do her work with less anxiety. Even my daughter’s teachers used Cailin’s guidance to modify their work with her. But most importantly, she became my daughter’s favorite resource. I can’t say how invaluable Cailin has been to my daughter’s progress and well-being. I’d recommend her a million times over. She is a gem.
-JUDE E.
My experience with Themba Tutors was awesome. When I was introduced to the service I told them my needs and based on that they set me up with a range of tutors to choose from. I chose to work with Paul who was the best tutor that I have ever worked with. I was studying for the New Jersey state teacher exam there was a number of subject areas that I had to study and one of them was math. Paul helped me understand the math on the test . He explained it to me in away that made it easy and he gave me tools to practice on my own. In addition to helping me with math skills he gave wonderful study tips and tricks to use to help me study the material that I had to learn. Paul was a pleasure to work with and O thank him for helping me pass the test.
-ESTHER B.
Chris has been wonderful working with U on math for the past few months, she adores him!
-Z.K.
My child worked with Gillian D virtually for math enrichment. She is an excellent teacher. She took time to understand my child’s specific learning style and provided tools that would be engaging. She was kind and empathetic- really made it her goal to connect with my child and build trust and rapport. My child started the school year with confidence and without the typically “brain-drain” that occurs over the summer, thanks to Gillian.
-NICOLE MAY
I want to thank you for the wonderful math tutoring you did with V! We really can see the changes in her self-confidence. It has been encouraging to see her improving her math grades. She is a big fan of yours, as are we. Because of the way LaGuardia HS is structuring classes for the year, V’s math class has now ended. Regardless, we will want Gillian to tutor V again when math officially starts up again in the fall.
-J.G.
MEET OUR GEOMETRY TUTORS WHO TRAVEL TO YOUR HOME

CAILIN
M.A. – Special Education

EVAN
Master’s in Leadership in Math Education, Bachelor’s Degree in Mathematics

JEFFREY
Master’s in Leadership in Math Education, Bachelor’s Degree in Mathematics

WILL
Master of Science, Special Education

AARON
Master’s in Math Education

MELISSA
Certified Math and Special Education Teacher, MS Math Education

LEAH
Bachelor’s degree in Secondary Education with a Concentration in Mathematics, M.S. in General and Special Education (grades 1-6)

TRACY
Certified Special Education Teacher

KARINA
Masters in Math Education
Chat with Themba Tutors Today!
Our Geometry Tutors work with all skill levels, travel to you, and offer remote tutoring services
FREE CONSULTATION WITH A GEOMETRY TUTOR!!!
Call: (917) 382-8641, Text: (833) 565-2370
Email: [email protected]
(we respond to email right away!).
References:
Craig Selinger
Latest posts by Craig Selinger (see all)
- Psychotherapy and Support Services at Cope With School NYC - April 12, 2024
- NYC Parents of Teens Support Group - April 8, 2024
- Here I Am, I Am Me: An Illustrated Guide to Mental Health - April 4, 2024







No Comments