
29 Nov 6th Grade Math Tutor – NYC Top Tutors
GRADE MATH TUTOR- NYC TOP TUTORS

WE travel to YOUR home:
We also travel to:
6th Grade Math Tutoring
So what exactly do students learn in 6th-grade math? We broke down 6th grade math into the following problems and topics, like breaking down a language into parts.
If you need checklists for a breakdown of 6th grade math, we highly recommend Khan Academy and IXL for Common Core Sixth-Grade Math Standards & K5 learning for their 6th Grade Worksheets. We also thank Embarc for breaking down 6th grade math into the following standards:
Module 1: Ratios and Unit Rates
Topic A: Representing and Reasoning About Ratios (6.RP.A.1, 6.RP.A.3a)
Lessons 1-8 Video Lectures:
https://youtu.be/rQfrcX5OQJE
https://youtu.be/KCL9yfg9T_g
https://youtu.be/Gfms4_pKSsk
https://youtu.be/MpJNY6aafO8
https://youtu.be/2ifWJb9jXJM
https://youtu.be/84r8ewqSVow
https://youtu.be/-tOopTkn5co
https://youtu.be/NkzJtqOLLwA
The Term Ratio
A 6th grade math tutor can help students develop an understanding and definition of the term ratio. A ratio is always a pair of numbers like 2:3 and never a pair of quantities like 2 cm:3 sec. They write the ratio in two forms: 2:3 or 2 to 3. They understand that order matters. If I am comparing 2 cm to 3 sec. Then I read and write the ratio 2:3 or 2 to 3. If I compare 3 sec to 3 cm, I write the ratio 3:2 or 3 to 2.
Example Problem and Solution
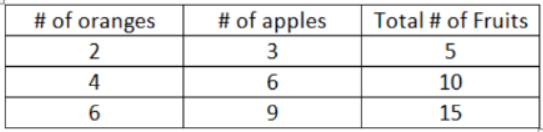
A recipe for fruit salad requires 2 oranges for every 3 apples. Write this situation as a ratio of oranges to apples.
Answer: The ratio of oranges to apples is 2:3. Students are encouraged to complete a table to show the relationship.
Students expand the table to show that there are other options to demonstrate 2 oranges for every 3 apples in the recipe.
Students are guided to articulate that there are 32 as many apples as there are oranges. Another way to articulate the same situation is that there are 23 as many apples as oranges. Students develop an intuitive understanding of equivalent ratios by using tape diagrams to explore possible quantities when one of the quantities is given. If the student is having a problem articulating ratio, a 6th grade math tutor can help.
Example Problem and Solution
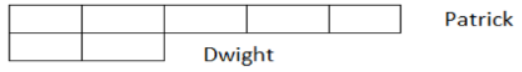
Patrick and Dwight are keeping track of the number of grams of sugar they consume daily as part of their diet regimen.
The ratio of the number of grams of sugar Patrick consumes to the number of grams of sugar Dwight consumes in a day is 5 to 2. If they consume 105 grams of sugar per day, how many grams do each consume? The tape diagram models the situation.
To determine how many grams of sugar each of them consumes, students need to know how many grams of sugar each of the sections of the tape diagram represents. Students divide the number of total grams of sugar they consume together (105 grams) by 7 total sections of the tape diagram.
105 divided by 7=15; therefore, each section of the tape diagram represents 15 grams of sugar.
Patrick consumes 75 grams of sugar per day (15 x 5), and Dwight consumes 30 grams of sugar per day (15 x 2).
Value of a Ratio
The ratios of 5:2 and 75:30 are not the same ratios, but we say they have the same value. The value of 75:30 is 5:2.
In our first example, 2:3 and 6:9 are not the same ratio, but we say the ratios have the same value.
A 6th grade math tutor can help students begin to apply a basic understanding of the relationship between ratios and fractions. We say if there are 2 boys to every 5 girls, then the fractional relationship is there are 25 as many boys as girls.
Words to Know:
Ratio – A pair of nonnegative numbers, A: B, where both are not zero, and that are used to indicate that there is a relationship between two quantities such that when there are A units of one quantity, there are B units of the second quantity.
Equivalent Ratios – Ratios that have the same value. Associated Ratios (e.g., if a popular shade of purple is made by mixing 2 cups of blue paint for every 3 cups of red paint, not only can we say that the ratio of blue paint to red paint in the mixture is 2:3, but we can discuss associated ratios such as the ratio of cups of red paint to cups of blue paint, the ratio of cups of blue paint to total cups of purple paint, the ratio of cups of red paint to total cups of purple paint, etc.)
Ratio Table – A table listing pairs of numbers that form equivalent ratios.
Topic B: Collections of Equivalent Ratios (6.RP.A.3a)
Lessons 9-15 Video Lectures:
https://youtu.be/QNd9lF-3nMQ
https://youtu.be/cuSJ6kq7V8M
https://youtu.be/AgbtqLEBQds
https://youtu.be/xjzj4DY5y24
https://youtu.be/ndaLh2U7-Xk
https://youtu.be/g0T01KV7F7I
Lesson 15: No video provided*
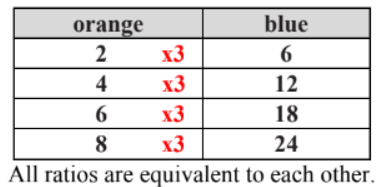
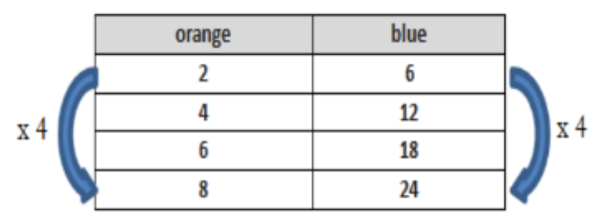
We can use repeated addition or multiplication to create a ratio table.
Students are to demonstrate an understanding of the additive and multiplicative properties of ratio tables. If adding a certain number to each entry in one column, you may need to add that same number to the entries in the other column and keep the same ratio. For example, in the ratio table above, 2 is added to the column labeled “Orange.” If we added 2 down the column labeled “Blue,” we would not get the same entries as the table.
Instead, the numbers you add to the entries must be related to the ratio used to make the table. However, if multiplying the entries in one column by a certain number, you can multiply the entries in the other column by the same number, and the ratio remains.
Ratio tables can be used to compare two ratios. You can do this by extending the table or comparing the values of the ratios. Students will build on their experience with number lines by representing collections of equivalent ratios on a double number line.
Example Problem and Solution
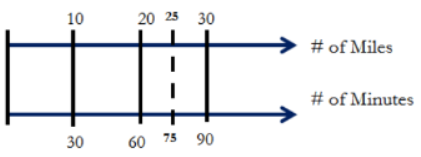
Julie has been biking at a constant speed for 30 minutes, during which time she traveled 10 miles. Julie would like to know how long it will take her to run 25 miles, assuming she maintains the same speed. Help Julie determine how long the trip will take. Include a table or diagram to support your answer.
Create a double number line using 10 miles and 30 minutes increments. 25 miles falls halfway between 20 and 30 miles, so its equivalent minutes would be between 60 and 90 miles, which is 75 miles. It will take Julie 75 minutes to travel 25 miles.
Example Problem and Solution
Paul wants to buy a new bike. The bike costs 52 more dollars than he has. If Paul charges $8 to cut grass, how many lawns will he have to cut to have enough money to buy his bike? Use a double-number line to support your answer.
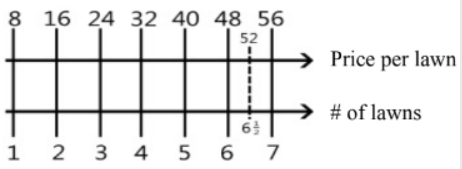
Students will relate their knowledge of ratio tables to equations using the value of the ratio.
Example Problem and Solution
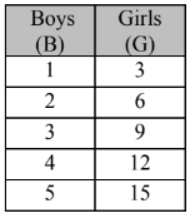
The ratio of boys to girls in Mrs. Smith’s math class is 1:3. Use the ratio table to create two equations that would show the relationship between the number of boys and the number of girls in the class.
There are three times as many girls in the class as boys. The equation to determine the number of girls in Mrs. Smith’s would be G = 3B.
There are 1/3 the number of boys in the class than girls. The equation to determine the number of boys in Mrs. Smith’s class would be B = 1⁄3G.
If there were 8 boys in the class, how many girls are there be? Use the equation to find your answer. Since you know the number of boys, you would use the formula G = 3B to find the answer. 3 x 8 boys = 24 girls. There are 24 girls in the class.
**A ratio table, equation, or double-number line diagram can be used to create ordered pairs. These ordered pairs can then be graphed on a coordinate plane to represent the ratio.
Example Problem and Solution
Using the ratio table from the previous example, graph the ordered pairs on the coordinate plane.
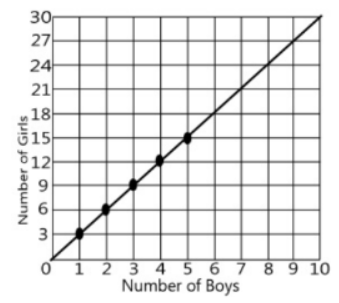
Ex: 1 boy to 3 girls creates the ordered pair
(1, 3) 2:6 creates (2, 6)…
What would be the number of boys if there were 24 girls in the class? To find the number of boys, find the y coordinate that matches up with 24 girls on the line. There are 8 boys in the class.
Words to Know:
Ratio – A pair of nonnegative numbers, A: B, where both are not zero, and that are used to indicate that there is a relationship between two quantities such that when there are A units of one quantity, there are B units of the second quantity.
Equivalent Ratios – Ratios that have the same value. Associated Ratios (e.g., if a popular shade of purple is made by mixing 2 cups of blue paint for every 3 cups of red paint, not only can we say that the ratio of blue paint to red paint in the mixture is 2:3, but we can discuss associated ratios such as the ratio of cups of red paint to cups of blue paint, the ratio of cups of blue paint to total cups of purple paint, the ratio of cups of red paint to total cups of purple paint, etc.)
Value of a Ratio– For the ratio A: B, the value of the ratio is the quotient A/B.
Ratio Table – A table listing pairs of numbers that form equivalent ratios.
Topic C: Unit Rates (6.RP.A.2, 6.RP.A.3b, 6.RP.A.3d)
Lessons 16-23 Video Lectures:
https://youtu.be/0hadBsQr57I
https://youtu.be/OZ-gjU1syqM
https://youtu.be/JeZabAdl-hE
https://youtu.be/jFoWjwBGzpI
https://youtu.be/CIxv7ywHKPM
https://youtu.be/kSosRf0rfO8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=chDROnw_09s
https://youtu.be/qRN6EStAD8E
Computing Unit Rate
The students recognize that they can associate a ratio of two quantities, such as 5 miles per 2 hours, to another quantity called the rate. Given a ratio, students precisely identify the associated rate. They identify the unit rate and the rate unit.
Example Problem and Answer
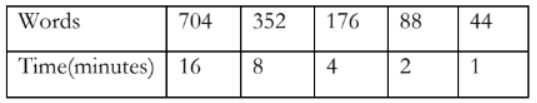
A publishing company is looking for new employees to type novels that will soon be published. The publishing company wants to find someone who can type at least 45 words per minute. Trent discovered he could type at a constant rate of 704 words in 16 minutes. Does Trent type at a fast enough rate to qualify for the job? Explain why or why not?
Answer:
After completing the table, students conclude that Trent can only type 44 words per minute which is slower than the 45 words per minute required.
Sample Problems:
How many words would Trent have to type in 20 minutes to qualify for the job? What is the rate unit for this problem?
Answer and Solution:
20 minutes x 45 words per minute = 900 words. Trent would have to type 900 words in 20 minutes to qualify for the job with the publishing company. The rate unit is words per minute.
Example Problem and Solution
Question:
At the Crystal Clean and Shine carwash, the average employee can wash 4 cars per hour. If the carwash wants to accommodate the large volume of customers that go through their business on a typical day, they must continue this rate for 8 hours. At this rate, how many cars can a typical employee wash in 8 hours?
Answer and Solution:
Students should be answering these questions:
At what rate does an average employee wash cars?
4 cars an hour
How long does the employee need to wash cars in order to keep up with the volume of customers on a typical Day?
8 hours.
Then, students multiply the rate (4 cars an hour) times the time (8 hours). 4 x 8 = 32. An average employee can wash 32 cars in 8 hours.
Students transfer this skill to convert measurements:
How many cups are in 5 quarts?
Percent as a Rate per 100
Students model percentages as a rate per hundred using 10 x 10 grids and write them as fractions over 100 or as a decimal. Students use the model to represent a percent; more importantly, they begin to connect and recognize the other representations of the same number in the form of a fraction and decimal.
Students solve problems by analyzing different unit rates given in tables, equations, and graphs.
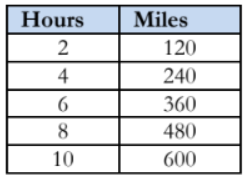
Question:
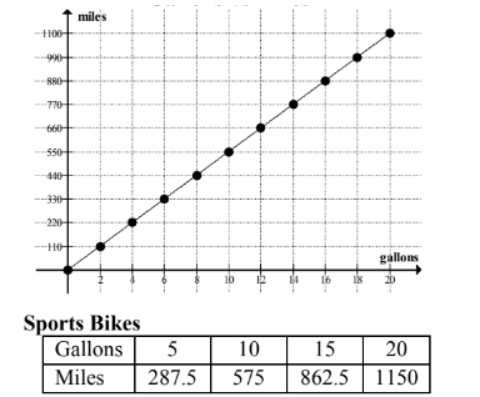
Emilio wants to buy a new motorcycle. He wants to compare the gas efficiency of each motorcycle before he makes a purchase. The dealerships presented the data below.
Leisure Bikes
Gallons vs Miles
Which motorcycle dealership has the most gas-efficient motorcycle? Use the graph and the table to make your decision.
Answer and Solution
At this point in the module, students are proficient in finding the unit rate from a graph and a table. They are encouraged to use a calculator to divide the quantities. In the graph of Leisure Bikes, a bike travels 110 miles on 2 gallons of gas; therefore, the unit rate is 55 miles per gallon. According to the values recorded in the table for Sports Bikes, their bike can travel 287.5 miles on 5 gallons of gas; therefore, the bike from Sports Bikes can travel 57.5 miles on one gallon of gas. Sports Bikes get 2.5 miles more per gallon of gas. Therefore, it is the most gas efficient.
Words to Know:
Ratio – A pair of nonnegative numbers, A: B, where both are not zero, and that are used to indicate there is a relationship between two quantities such that when there are A units of one quantity, there are B units of the second quantity.
Rate – A rate indicates, for a proportional relationship between two quantities, how many units of one quantity there are for every 1 unit of the second quantity. For a ratio of A:B between two quantities, the rate is A/B units of the first quantity per unit of the second quantity.
Unit Rate – The numeric value of the rate, e.g., in the rate of 2.5 mph, the unit rate is 2.5.
Value of a Ratio – The value of a ratio is a ratio whose denominator is one. The value of the ratio 9:3 is 3:1.
Ratio table – A table of values listing pairs of numbers that form equivalent ratios.
Rate Unit– Miles per hour; dollars per pound; words per minute
Topic D: Percent (6.RP.A.3c)Lessons 24-29
Video Lectures:
https://youtu.be/F7ILa1KBY7c
https://youtu.be/5vVcvvfAJiI
https://youtu.be/j6PY5SgBU3A
https://youtu.be/9Zm_6B-ImrY
https://youtu.be/jGWPqYvtu04
https://youtu.be/te82PvYBxJ0
Part-to-Whole Ratio
Students understand that percentages are related to part-to-whole ratios and rates where the whole is 100. Students model percentages and write a percent as a fraction over 100 or a decimal to the hundredth place.
Example Problem and Answer
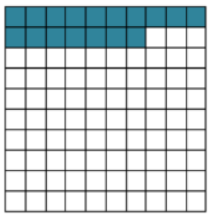
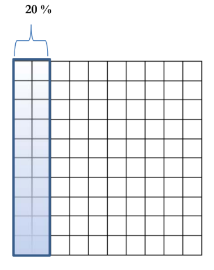
Imagine you are shopping. You want to purchase an item for $100. Today it is 20% off of the original price. What does this mean?
Answer:
What does the grid show?
100 blocks.
How many are shaded?
20 blocks.
How many are not shaded?
80 blocks.
How can we use this model to help us think about 20% off of $100.00?
From the grid, we can see that when I save 20%, I am paying 80% of the original value. We can see I would be saving $20 and paying $80 when a $100 item is 20% off.
Students write a fraction and a decimal as a percent of a whole quantity and write a percent of a whole quantity as a fraction or decimal.
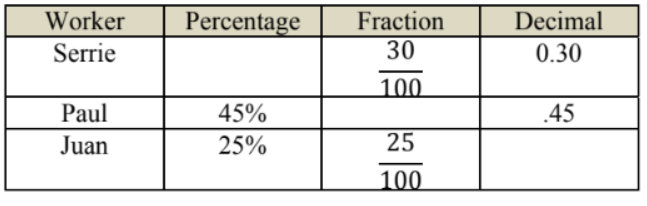
Example Problem and Solution
Star Middle school was having a Spring Fair. Terry was responsible for the workers in the dunking booth. Here is a list of the workers and the percentage of time they would have to work. Complete the table with the missing values.
Answer: Serrie – Percentage is 30%
Paul – Fraction is 45100
Juan – Decimal is .25
Words to Know:
Rate – A rate indicates, for a proportional relationship between two quantities, how many units of one quantity there are for every 1 unit of the second quantity. For a ratio of A:B between two quantities, the rate is A/B units of the first quantity per unit of the second quantity.
Unit Rate – The numeric value of the rate, e.g., in the rate of 2.5 mph, the unit rate is 2.5.
Percent– Rate per hundred
*The following information was obtained from Embarc.Online (a website that was originally created to support local teachers using Eureka Math, but we now serve 30,000 users each day across the nation). This information applies to all math users.
TESTIMONIALS
Paul at Themba has been an exceptional tutor for my son, both in terms of teaching the subject matter and teaching how best to approach the process of learning math and executing assignments. We feel very fortunate to be working with Paul.
-Michael Birnbaum
We have been with our tutor, Cailin, for two years, from 5th – 7th grade. She started as an executive functioning tutor with my daughter. From the start, she demonstrated a depth of expertise and a selective use of techniques skillfully adapted to my daughter’s ADHD and mth disability. Cailin made math accessible and understandable to her in a way that even her teachers had not been able to do. She differentiated reading, writing and math tasks and assignments to tailor them to my daughter’s unique learning differences. Not only did it have an effect on her grades and her work efficiency, but she finally could do her work with less anxiety. Even my daughter’s teachers used Cailin’s guidance to modify their work with her. But most importantly, she became my daughter’s favorite resource. I can’t say how invaluable Cailin has been to my daughter’s progress and well-being. I’d recommend her a million times over. She is a gem.
-Jude E.
I thought Paul was terrific and our son did too! Paul was particularly helpful on the math section of the ACT and math in general. Paul had an amazing rapport with our son, and that made the twice weekly commitment, for tutoring, fine for our son, which is really important. We highly recommend Paul!
-Martha P.
My son, a junior in a private high school worked, with a wonderful tutor from Themba to get ready for his SATs. I spoke with Blythe and she asked detailed questions about my sons strengths and weaknesses. She put me in touch with Don, who worked beautifully with my son. Don immediately understood where my son needed help and focused their time together on specific areas of need. He also recognized my sons strengths ( math )and was able to accelerate his understanding in those areas. My sons score jumped 190 points! The individualized instruction he got from Themba and Don was amazing! I highly recommend these wonderful people.
-Marie W.
This company is great in finding awesome learning specialists who work with kids of all ages and use multisensory techniques to help break down abstract concepts. My child needs help with math and they were able to supply my child with a top-notch math tutor who was able to really help my son improve. Not only is it hard to find qualified math learning specialists who work well with school aged children, but they come to your home, which is a real godsend.
-Mr. K. Kim
MEET OUR NYC TOP TUTORS WHO COULD COME TO YOUR HOME

MELISSA
Certified Math and Special Education Teacher, MS Math Education

AARON
Master’s in Math Education

LEAH
Bachelor’s degree in Secondary Education with a Concentration in Mathematics, M.S. in General and Special Education (grades 1-6)

JEFFREY
Master’s in Mathematics Education(5-9)

WILL
Master of Science, Special Education

TRACY
Certified Special Education Teacher

EVAN
Master’s in Leadership in Math Education, Bachelor’s Degree in Mathematics

KARINA
Masters in Math Education

CAILIN
M.A. – Special Education
LEARN MORE ABOUT MATH TUTORING SERVICES:
⏩ Long Island Math Tutoring
⏩ Upper East Side Math Tutoring
⏩ North and Central NJ Math Tutoring
⏩ Long Island Middle and High School Math Tutoring
⏩ Hudson, County NJ Middle and High School Math Tutoring
⏩ Manhattan Middle and High School Math Tutoring
⏩ Bronx Middle and High School Math Tutoring
⏩Manhattan In-home Math Tutoring
⏩ Best Brooklyn Math Tutors
⏩ Remote IB Math Tutoring
Chat with Themba Tutors Today! Our 6th Grade Math Tutors are ready to help you right now!
FREE CONSULTATION WITH A NYC TUTOR!!!
Call: (917) 382-8641, Text: (833) 565-2370
Email: [email protected]
(we respond to email right away!).
Craig Selinger
Latest posts by Craig Selinger (see all)
- Psychotherapy and Support Services at Cope With School NYC - April 12, 2024
- NYC Parents of Teens Support Group - April 8, 2024
- Here I Am, I Am Me: An Illustrated Guide to Mental Health - April 4, 2024





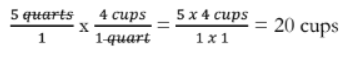
No Comments